ckan-docker: Addons
Debugging
Debugging CKAN Development Instance with VSCode Dev Containers and debugpy
The Visual Studio Code Dev Containers extension is a powerful tool that enables developers to use a container as a complete development environment. With this extension, developers can open any folder inside a container and take advantage of the full range of features provided by Visual Studio Code. To do this, developers create a devcontainer.json file in their project that specifies how to access or create a development container with a predefined tool and runtime stack. This allows developers to work in an isolated environment, ensuring that the development environment is consistent across team members and that project dependencies are easy to manage.
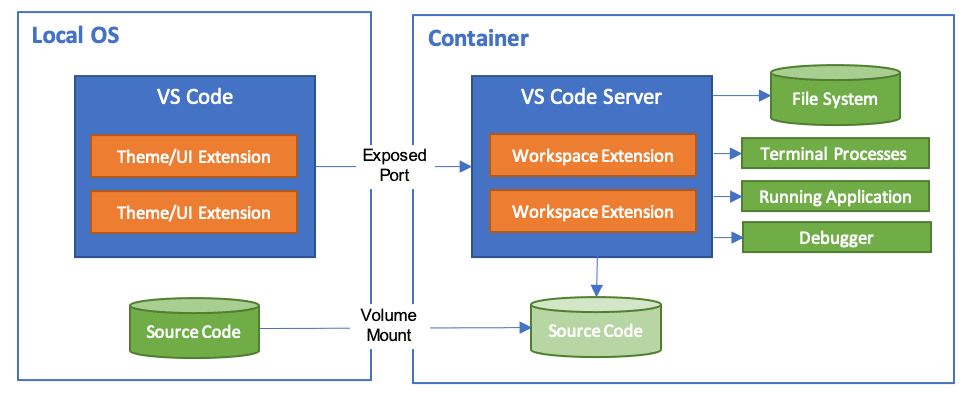
To set this up:
-
Install VSCode.
-
Install the Remote Development extension for VSCode.
-
In your project directory, create a
devcontainer.jsonfile. This file will contain the configuration for your development container. -
In the
devcontainer.jsonfile, specify the Docker image for your development container and any additional configuration settings, such as environment variables, ports to expose, and startup commands. -
Enable
debugpyfor your development instance in your.envfile:
USE_DEBUGPY_FOR_DEV=true
-
Start the containers in development mode and launch VS Code.
-
Install the "Dev Container" extension: press
CTRL+SHIFT+X, type "dev container", click "install". -
Click the
Open a Remote Windowbutton in the bottom-left of the VS Code window. -
Click
Attach to Running Container...and select your ckan-dev container, e.g.ckan-docker-ckan-dev-1. -
Click the
Run and Debugicon on the left panel thencreate a launch.json, selectPython Debugger,Remote Attach, hostlocalhostand port5678. -
Press
F5or click theRunmenu andStart Debugging.
You can now set breakpoints and remote debug your CKAN development instance using VSCode Dev Containers and debugpy.
pdb
Add these lines to the ckan-dev service in the docker compose.dev.yml file
ports:
- "0.0.0.0:${CKAN_PORT}:5000"
stdin_open: true
tty: true
Debug with pdb (example) - Interact with docker attach $(docker container ls -qf name=ckan)
command: python -m pdb /usr/lib/ckan/venv/bin/ckan --config /srv/app/ckan.ini run --host 0.0.0.0 --passthrough-errors
Reverse proxy
NGINX
The default Docker Compose configuration (docker-compose.yml) uses an NGINX image as the front-end (ie: reverse proxy). It includes HTTPS running on port number 8443 and an HTTP port (81). A "self-signed" SSL certificate is generated beforehand and the server certificate and key files are included. The NGINX server_name (ENV: PROXY_SERVER_NAME) directive and the CN field in the SSL certificate have been both set to 'localhost'. This should obviously not be used for production.
The proxy locations, ports and other NGINX options can be modified in the .env file:
# Host Ports
NGINX_PORT_HOST=81
NGINX_SSLPORT_HOST=8443
# NGINX
NGINX_PORT=80
NGINX_SSLPORT=443
NGINX_LOG_DIR=/var/log/nginx
# Check CKAN__ROOT_PATH and CKANEXT__DCAT__BASE_URI. If you don't need to use domain locations, it is better to use the nginx configuration. Leave blank or use the root `/`.
PROXY_SERVER_NAME=localhost
PROXY_CKAN_LOCATION=/catalog
PROXY_PYCSW_LOCATION=/csw
The base Docker Compose configuration uses an NGINX image as the front-end (ie: reverse proxy). It includes HTTPS running on port number 8443. A "self-signed" SSL certificate is generated as part of the ENTRYPOINT. The ENV PROXY_SERVER_NAME, NGINX server_name directive and the CN field in the SSL certificate have been both set to 'localhost'. This should obviously not be used for production.
Creating the SSL cert and key files as follows:
openssl req -new -newkey rsa:4096 -days 365 -nodes -x509 -subj "/C=DE/ST=Berlin/L=Berlin/O=None/CN=localhost" -keyout ckan-local.key -out ckan-local.crt
The ckan-local.* files will then need to be moved into the nginx/setup/ directory
Apache HTTP Server
The Docker Compose configuration (docker-compose.apache.yml) uses an httpd image as the front-end. It has two routes for the ckan (default location: /catalog) and ckan-pycsw (default location: /csw) services.
The proxy locations, ports and other Apache Web Server options can be modified in the .env file:
# Host Ports
APACHE_PORT_HOST=81
# Apache HTTP Server
APACHE_VERSION=2.4-alpine
APACHE_PORT=80
APACHE_LOG_DIR=/var/log/apache
# Check CKAN__ROOT_PATH and CKANEXT__DCAT__BASE_URI. If you don't need to use domain locations, it is better to use the nginx configuration. Leave blank or use the root `/`.
PROXY_SERVER_NAME=localhost
PROXY_CKAN_LOCATION=/catalog
PROXY_PYCSW_LOCATION=/csw
envvars
The ckanext-envvars extension is used in the CKAN Docker base repo to build the base images. This extension checks for environmental variables conforming to an expected format and updates the corresponding CKAN config settings with its value.
For the extension to correctly identify which env var keys map to the format used for the config object, env var keys should be formatted in the following way:
All uppercase
Replace periods ('.') with two underscores ('__')
Keys must begin with 'CKAN' or 'CKANEXT', if they do not you can prepend them with 'CKAN___'
For example:
CKAN__PLUGINS="envvars image_view text_view recline_view datastore datapusher"CKAN__DATAPUSHER__CALLBACK_URL_BASE=http://ckan:5000CKAN___BEAKER__SESSION__SECRET=CHANGE_ME
These parameters can be added to the .env file
For more information please see ckanext-envvars
When deploying under a proxy, such as in a corporate environment, to avoid errors when resolving urls with container_names/hostnames associated with the container on internal networks, use the no_proxy variable, in lower case, with the names of the services/containers, the IP of the Docker network, etc.
e.g:
no_proxy="127.0.0.1,192.168.192.0/23,172.0.0.0/0,redis,solr,${DB_CONTAINER_NAME}"`
Datastore
The Datastore database and user is created as part of the entrypoint scripts for the db container.
xloader
This deployment replaces DataPusher with XLoader using Supervisor, more info about other alternatives on the wiki page for this: https://github.com/ckan/ckan-docker/wiki/Replacing-DataPusher-with-XLoader
ckan-pycsw
ckan-pycsw is a docker compose environment (based on pycsw) for development and testing with CKAN Open Data portals.
Available components:
- pycsw: The pycsw app. An OARec and OGC CSW server implementation written in Python.
- ckan2pycsw: Software to achieve interoperability with the open data portals based on CKAN. To do this, ckan2pycsw reads data from an instance using the CKAN API, generates ISO-19115/ISO-19139 metadata using pygeometa, or a custom schema that is based on a customized CKAN schema, and populates a pycsw instance that exposes the metadata using CSW and OAI-PMH.
Harvester consumers on a deployed CKAN
ckanext-harvest supervisor allows you to harvest metadata from multiple sources on a production deployment. Here it is deployed by a worker consumers in the ckan container, also the ckanext-harvest extension and other custom harvesters (ckanext-schemingdcat or ckanext-dcat) are included in the CKAN docker images.
To enable harvesters you need to set up in the .env file the CKAN__PLUGINS variable with the harvest plugin: https://github.com/mjanez/ckan-docker/blob/a18e0c80d9f16b6d9b6471e3148d48fcb83712bd/.env.example#L126-L127
ckan-docker: Tips
CKAN. Backups
PostgreSQL offers the command line tools pg_dump and pg_restore for dumping and restoring a database and its content to/from a file.
Backup service for db container
-
Create a new file called
ckan_backup_custom.shand open it in your preferred text editor. -
Add the following code to the script, replacing the placeholders with your actual values:
#!/bin/bash
# Set the necessary variables
CONTAINER_NAME="db"
DATABASE_NAME="ckandb"
POSTGRES_USER="postgres"
POSTGRES_PASSWORD="your_postgres_password"
BACKUP_DIRECTORY="/path/to/your/backup/directory"
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d%H%M%S)
MONTH=$(date +%m)
YEAR=$(date +%Y)
# Create the monthly backup directory if it doesn't exist
mkdir -p "$BACKUP_DIRECTORY/monthly/$YEAR-$MONTH"
# Run the backup command
docker exec -e PGPASSWORD=$POSTGRES_PASSWORD $CONTAINER_NAME pg_dump -U $POSTGRES_USER -Fc $DATABASE_NAME > "$BACKUP_DIRECTORY/monthly/$YEAR-$MONTH/ckan_backup_$DATE.dump"
# Compress the dump files into a zip archive
cd "$BACKUP_DIRECTORY/monthly/$YEAR-$MONTH" || exit
zip "backup_${YEAR}-${MONTH}.zip" *.dump
# Remove the original dump files
rm -f *.dump -
Replace the following placeholders with your actual values:
your_postgres_password: The password for the PostgreSQL user./path/to/your/backup/directory: The path to the directory where you want to store the backup files.
warningIf you have changed the values of the PostgreSQL container, database or user, change them too. Check that
zippackage is installed:sudo apt-get install zip -
Save and close the file.
-
Make the script executable:
chmod +x ckan_backup_custom.sh -
Open the
crontabfor the current user:crontab -e -
Add the following line to schedule the backup to run daily at midnight (adjust the schedule as needed):
0 0 * * * /path/to/your/script/ckan_backup_custom.shnoteReplace
/path/to/your/scriptwith the actual path to theckan_backup_custom.shscript. -
Save and close the file.
The cronjob is now set up and will backup your CKAN PostgreSQL database daily at midnight using the custom format. The backups will be stored in the specified directory with the timestamp in the filename.
Sample scripts for backing up CKAN: doc/scripts
Restore a backup
If need to use a backup, restore it:
-
First clean the database. Caution, this will delete all data from your CKAN database!
docker exec -it ckan /bin/bash -c "export TERM=xterm; exec bash"
# Delete everything in the CKAN database, including the tables, to start from scratch
ckan -c $CKAN_INI db clean -
After cleaning the database you must do either initialize it or import a previously created dump.
docker exec -i -e PGPASSWORD=$POSTGRES_PASSWORD $POSTGRESQL_CONTAINER_NAME pg_restore -U $POSTGRES_USER --clean --if-exists -d $DATABASE_NAME < /path/to/your/backup/directory/ckan.dump -
Restart the
ckancontainer.
CKAN. Manage new users
-
Create a new user from the Docker host, for example to create a new user called
user_exampledocker exec -it <container-id> ckan -c ckan.ini user add user_example email=user_example@localhost
# Admin user
docker exec -it <container-id> ckan -c ckan.ini sysadmin add admin_example email=admin_example@localhost name=admin_exampleTo delete the 'user_example' user
docker exec -it <container-id> ckan -c ckan.ini user remove user_example` -
Create a new user from within the ckan container. You will need to get a session on the running container
ckan -c ckan.ini user add user_example email=user_example@localhost`To delete the 'user_example' user
ckan -c ckan.ini user remove user_example`
Docker Compose. Configure a docker compose service to start on boot
To have Docker Compose run automatically when you reboot a machine, you can follow the steps below:
-
Create a systemd service file for Docker Compose. You can create a file named
ckan-docker-compose.servicein the/etc/systemd/system/folder with the following content:[Unit]
Description=CKAN Docker Compose Application Service
Requires=docker.service
After=docker.service
[Service]
User=docker
Group=docker
Type=oneshot
RemainAfterExit=yes
WorkingDirectory=/path/to/project/ckan-docker/
ExecStart=/bin/docker compose up -d
ExecStop=/bin/docker compose down
TimeoutStartSec=0
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target -
Replace
/path/to/project/ckan-docker/with the path where your project'sdocker-compose.ymlfile is located and and check the path to the docker compose binary on execution and stop:/bin/docker. Also change theUser/Groupto execute the service. -
Load the systemd service file with the following command:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload -
Enables the service to start automatically when the machine boots up:
sudo systemctl enable ckan-docker-compose -
You can now start the service with the following command:
sudo systemctl start ckan-docker-compose -
If you want to stop or check the status of the service, use the following commands:
# Stop the service
sudo systemctl stop ckan-docker-compose
# Check the status
sudo systemctl status ckan-docker-compose