ckan-docker: Enhancements
CKAN images
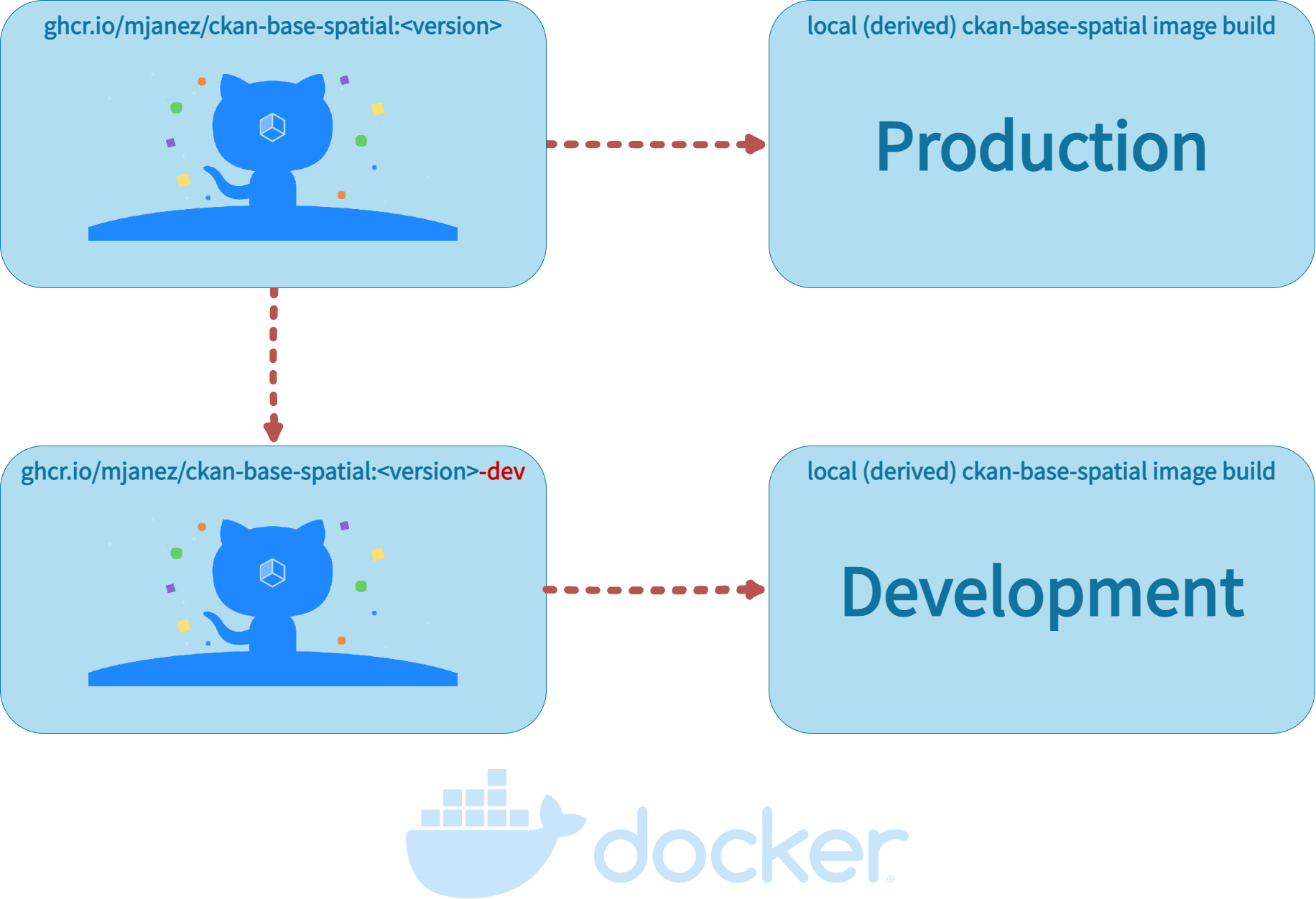
The Docker image config files used to build your CKAN project are located in the ckan/ folder. There are two Docker files:
-
Dockerfile: this is based onmjanez/ckan-base-spatial:<version>, a base image located in the Github Package Registry, that has CKAN installed along with all its dependencies, properly configured and running on uWSGI (production setup) -
Dockerfile.dev: this is based onmjanez/ckan-base-spatial:<version>-devalso located located in the Github Package Registry, and extendsmjanez/ckan-base-spatial:<version>to include:- Any extension cloned on the
./srcfolder will be installed in the CKAN container when booting up Docker Compose (docker compose up). This includes installing any requirements listed in arequirements.txt(orpip-requirements.txt) file and runningpython setup.py develop. - CKAN is started running this:
/usr/bin/ckan -c /srv/app/ckan.ini run -H 0.0.0.0. - Make sure to add the local plugins to the
CKAN__PLUGINSenv var in the.envfile.
- Any extension cloned on the
-
Any custom changes to the scripts run during container start up can be made to scripts in the
setup/directory. For instance if you wanted to change the port on which CKAN runs you would need to make changes to the Docker Compose yaml file, and thestart_ckan.sh.overridefile. Then you would need to add the following line to the Dockerfile ie:COPY setup/start_ckan.sh.override ${APP_DIR}/start_ckan.sh. Thestart_ckan.shfile in the locally built image would override thestart_ckan.shfile included in the base image
If you get an error like doesn't have execute permissions:
Daemon error response: failed to create shim task: OCI runtime create failed: runc create failed: unable to start container process: exec: "/srv/app/start_ckan.sh": permission denied: unknown
It may be necessary to give execute permissions to the file in the Dockerfile:
...
# Override start_ckan.sh
COPY setup/start_ckan.sh.override ${APP_DIR}/start_ckan.sh
RUN chmod +x ${APP_DIR}/start_ckan.sh
...
CKAN images enhancement
Extending the base images
You can modify the docker files to build your own customized image tailored to your project, installing any extensions and extra requirements needed. For example here is where you would update to use a different CKAN base image ie: ckan/ckan-base-spatial:<new version>
To perform extra initialization steps you can add scripts to your custom images and copy them to the /docker-entrypoint.d folder (The folder should be created for you when you build the image). Any *.sh and *.py file in that folder will be executed just after the main initialization script (prerun.py) is executed and just before the web server and supervisor processes are started.
For instance, consider the following custom image:
ckan
├── docker-entrypoint.d
│ └── setup_validation.sh
├── Dockerfile
└── Dockerfile.dev
We want to install an extension like ckanext-validation that needs to create database tables on startup time. We create a setup_validation.sh script in a docker-entrypoint.d folder with the necessary commands:
#!/bin/bash
# Create DB tables if not there
ckan -c /srv/app/ckan.ini validation init-db
And then in our Dockerfile.dev file we install the extension and copy the initialization scripts:
FROM ckan/ckan-base-spatial:2.9.11
RUN pip install -e git+https://github.com/frictionlessdata/ckanext-validation.git#egg=ckanext-validation && \
pip install -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/frictionlessdata/ckanext-validation/master/requirements.txt
COPY docker-entrypoint.d/* /docker-entrypoint.d/
There are a number of extension examples commented out in the Dockerfile.dev file
Applying patches
When building your project specific CKAN images (the ones defined in the ckan/ folder), you can apply patches
to CKAN core or any of the built extensions. To do so create a folder inside ckan/patches with the name of the
package to patch (ie ckan or ckanext-??). Inside you can place patch files that will be applied when building
the images. The patches will be applied in alphabetical order, so you can prefix them sequentially if necessary.
For instance, check the following example image folder:
ckan
├── patches
│ ├── ckan
│ │ ├── 01_datasets_per_page.patch
│ │ ├── 02_groups_per_page.patch
│ │ ├── 03_or_filters.patch
│ └── ckanext-harvest
│ └── 01_resubmit_objects.patch
├── setup
├── Dockerfile
└── Dockerfile.dev
Git diff is a command to output the changes between two sources inside the Git repository. The data sources can be two different branches, commits, files, etc.
- Show changes between working directory and staging area:
git diff > [file.patch] - Shows any changes between the staging area and the repository:
git diff --staged [file]`
Applying patches in dev mode
To apply patches in development mode, you would need to follow these steps:
-
Ensure that your patches are placed in the
ckan/patchesdirectory. The patches should be organized into subdirectories named after the package they are intended to patch (e.g.,ckanorckanext-??). Each patch file should end with the .patch extension.For example, your directory structure might look like this:
ckan
├── patches
│ ├── ckan
│ │ ├── 01_datasets_per_page.patch
│ │ ├── 02_groups_per_page.patch
│ │ ├── 03_or_filters.patch
│ └── ckanext-harvest
│ └── 01_resubmit_objects.patch
├── setup
├── Dockerfile
└── Dockerfile.dev -
Navigate to the
/srcdirectory. -
Apply the patches using the patch command:
find /path/to/ckan/patches -name '*.patch' -exec patch -p1 < {} \;This command will recursively search the
/path/to/ckan/patchesdirectory for files ending with.patchand apply them using the patch command. Replace/path/to/ckan/patcheswith the actual path to yourckan/patchesdirectory.
Create an extension in development mode
You can use the ckan extension instructions to create a CKAN extension, only executing the command inside the CKAN container and setting the mounted src/ folder as output:
docker compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml exec ckan-dev /bin/sh -c "ckan -c /srv/app/ckan.ini generate extension --output-dir /srv/app/src_extensions"
Then, answer the prompts to configure the plugin:
Extension's name [must begin 'ckanext-']: ckanext-newextension
Author's name []: Joe Bloggs
Author's email []: joe@bloggs.com
Your Github user or organization name []: joebloggs
Brief description of the project []: test creating a new extension
List of keywords (separated by spaces) [CKAN]: ckanext-newextension
Do you want to include code examples? [y/N]: y
Written: /srv/app/src_extensions/ckanext-newextension
The new extension files and directories are created in the /srv/app/src_extensions/ folder in the running container. They will also exist in the local src/ directory as local /src directory is mounted as /srv/app/src_extensions/ on the ckan container. You might need to change the owner of its folder to have the appropiate permissions.